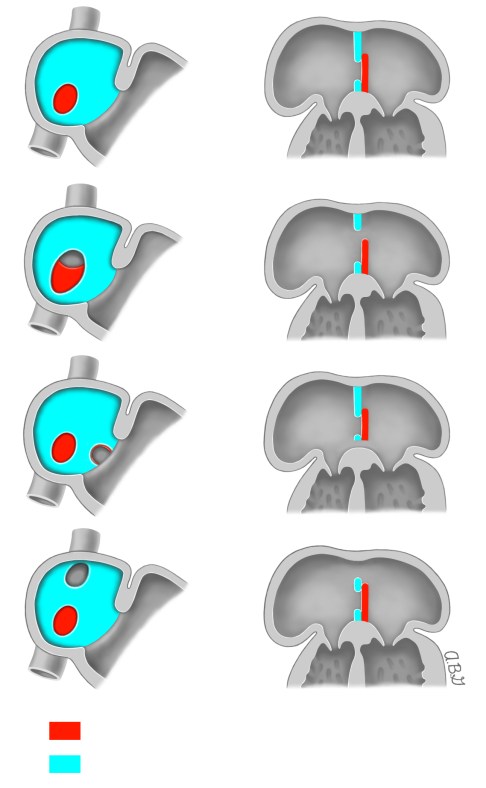
Atrial Septal Defects – The normal atrial septum (panel A) as well as various types of atrial septal defects (ASD) are shown. Panel B: secundum ASD is formed by the poor growth of the septum secundum or excessive absorption of the septum primum. Panel C: Primum ASD is formed by the failure of the septum primum to fuse with the endocardial cushions. The fossa ovalis is normal. The frontal view of the primum ASD shows the caudal location of the ASD just above the endocardial cushion. Panel D: Sinus venosus ASD is caused by the malposition of the insertion of the superior or inferior vena cava and is outside the area of the fossa ovalis. Reproduced with permission from: Vick GW, Bezold LI. Management and outcome of isolated atrial septal defects in children. In: UpToDate, Basow DS (Ed), UpToDate, Waltham, MA 2013. Copyright © 2013 UpToDate, Inc. For more information visit http://www.uptodate.com.
Nov 4
Published at 1292 × 2096 in Chapter 3. Congenital Heart Disease
Posted on November 4, 2013. Bookmark the permalink. Leave a comment.
Leave a comment
Comments 0